John K Pearman, Laura Biessy, Georgia Thomson-Laing, Sean Waters, Marcus J Vandergoes, Jamie D Howarth, Andrew Rees, Chris Moy, Xavier Pochon, Susanna A Wood, Local factors drive bacterial and microeukaryotic community composition in lake surface sediment collected across an altitudinal gradient, FEMS Microbiology Ecology, Volume 96, Issue 6, June 2020, fiaa070, https://doi.org/10.1093/femsec/fiaa070
Abstract
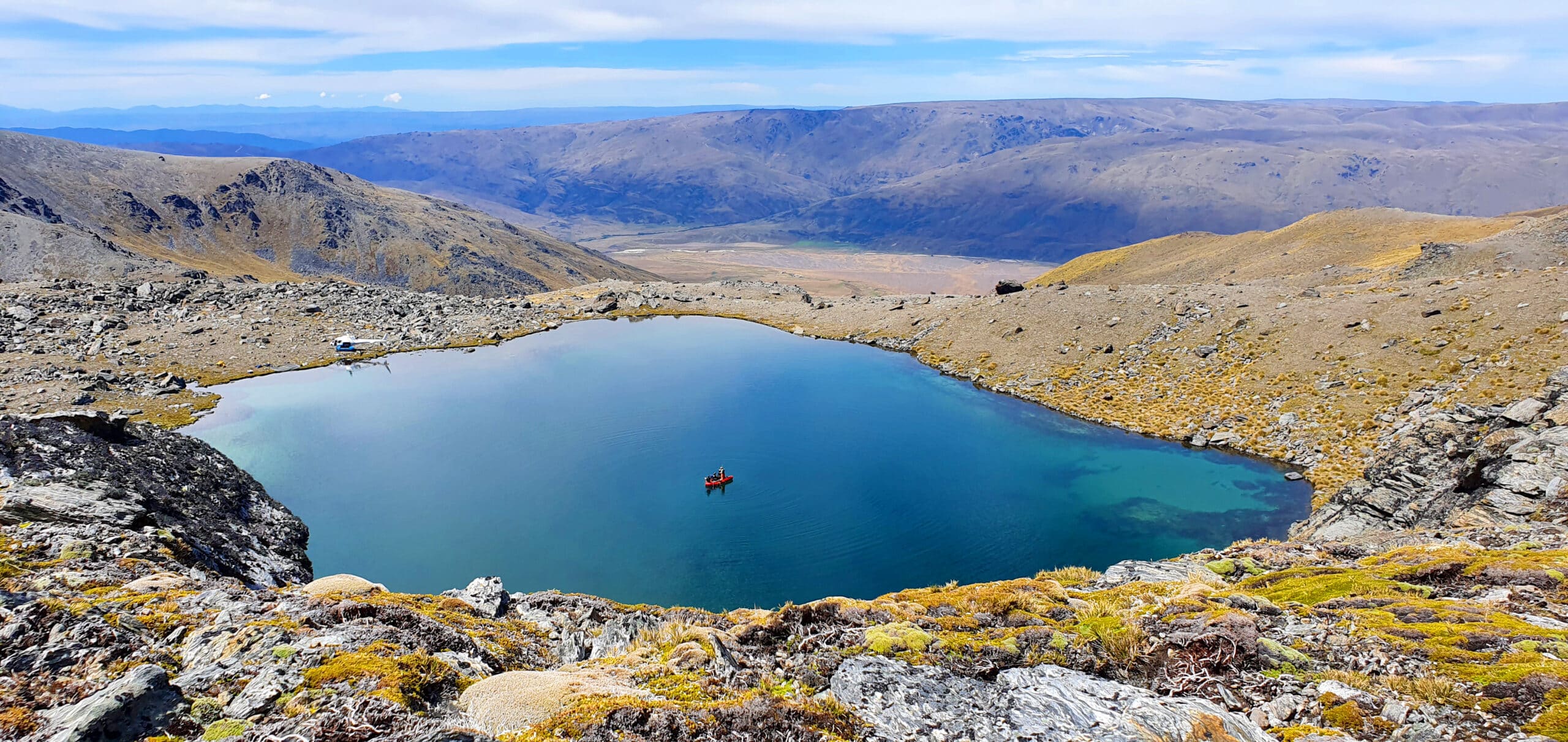
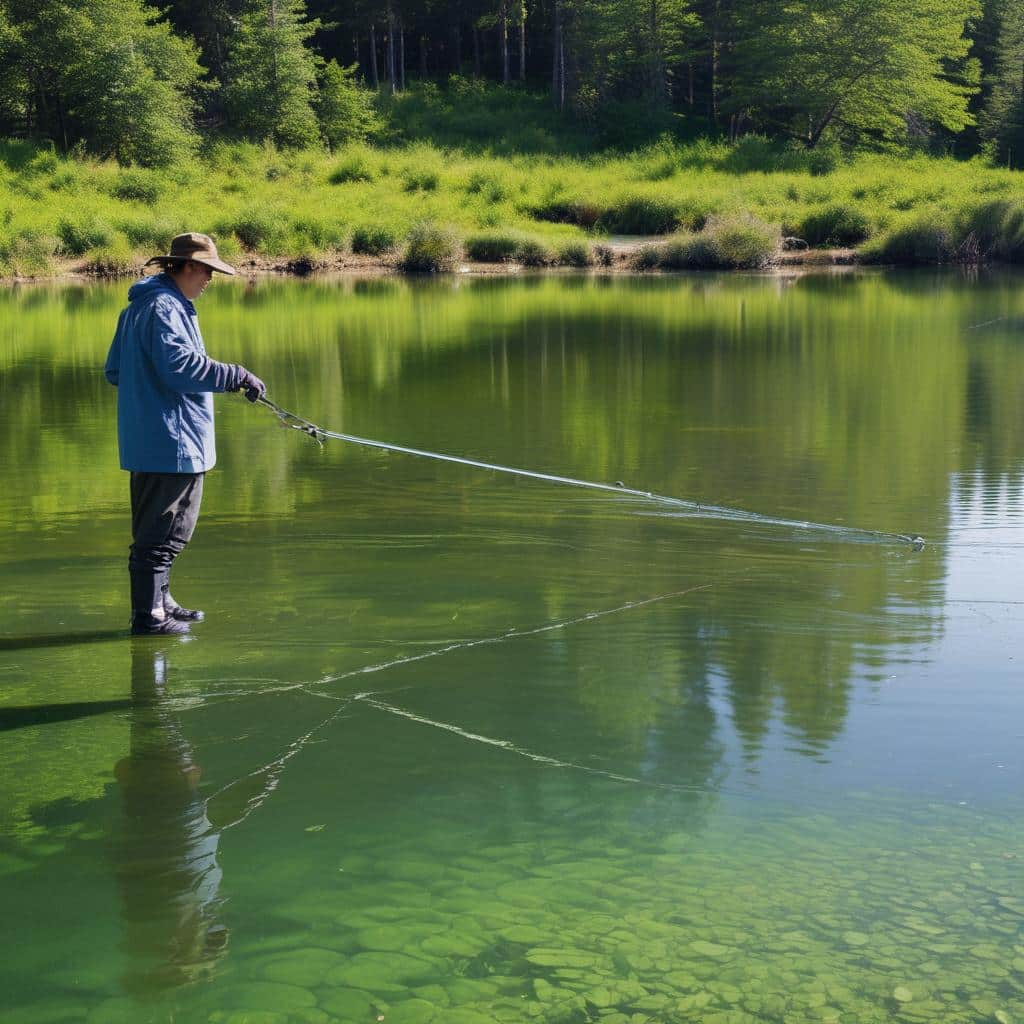
Lake surface sediments are dominated by microorganisms that play significant roles in biogeochemical cycling within lakes. There is limited knowledge on the relative importance of local environmental factors and altitude on bacterial and microeukaryotic community richness and composition in lake sediments. In the present study, surface sediment samples were collected from 40 lakes along an altitude gradient (2–1215 m). Microbial communities were characterized using 16S (bacteria) and 18S (microeukaryotes) rRNA gene metabarcoding. Bacterial and microeukaryotic richness were not correlated with altitude but instead to environmental variables (e.g. area of water in the catchment (bacteria: R = −0.43). For both bacteria and microeukaryotes, dissimilarity in the community structure had a higher correlation to combined environmental variables (without altitude) (bacteria: R = 0.53; microeukaryotes: R = 0.55) than altitude alone (bacteria: R = 0.34; microeukaryotes: R = 0.47). Sediment sulfur and productive grassland were important variables in determining the relative abundance of sulfate reducing bacteria. Nitrospira, was positively related to altitude but negatively to water column total organic carbon and the proportion of productive grassland in the catchment. Little overlap in amplicon sequence variants was shown amongst lakes. This has important considerations for management decisions, suggesting that to protect biodiversity, conservation of numerous lakes and lake types is required.