DOI: 10.1021/acs.est.2c06835
Abstract
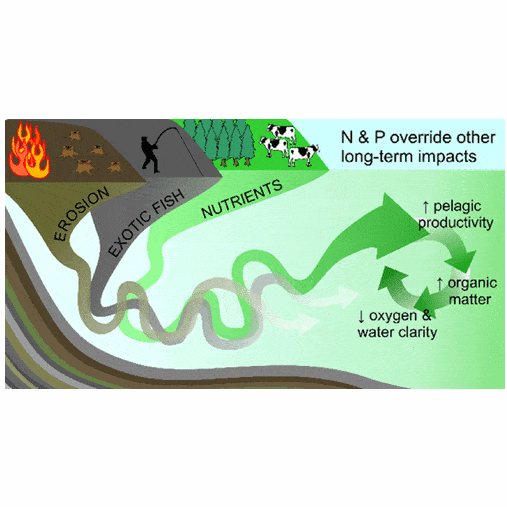
Interactions among multiple stressors, legacies of past perturbations, and the lack of historical information make it difficult to determine the influence of individual anthropogenic impacts on lakes and separate them from natural ecosystem variability. In the present study, we coupled paleolimnological approaches, historical data, and ecological experiments to disentangle the impacts of multiple long-term stressors on lake ecosystem structure and function. We found that the lake structure and function remained resistant to the impacts of catchment deforestation and erosion, and the introduction of several exotic fish species. Changes in ecosystem structure and function were consistent, with nutrient enrichment being the primary driver of change. Significant and sustained changes in the lake diatom community structure (and their nutrient requirements), bacterial community function, and paleolimnological proxies of ecosystem function coincided with nitrogen and phosphorus fertilizers in the catchment. The results highlight that the effects of increased nutrient inputs are much stronger than the influence of other, potentially significant, drivers of ecosystem change, and that the degree of nutrient impact can be underestimated by environmental monitoring due to its diffuse and accumulative nature. Delineating the effects of multiple anthropogenic drivers requires long-term records of both impacts and lake ecosystem change across multiple trophic levels.




